4. Resource Sharing: Multiple Access
- -
Network Links
- Broadcast link/shared medium
- Example : Ethernet, wireless local area networks (LANs)
💡whenanyone transmitsa frame, the channel broadcasts the frame and each of the other nodes receives acopyComputer network broadcast channel은
송신과 수신이 동시에 가능하다. 반면 television의 경우에는 one-way broadcast이다.
하지만, broadcast link의 경우에는 공유자원인 broadcast link 를 나눠서 써야한다는 측면때문에 multiple access problem 이 발생한다.
Multiple Access Problem
Problem definition
Receiving multiple frames at the same time : collision
→ 여러 frame이 동시에 들어와 서로 충돌하면서 하나의 혼합된 신호로 섞이게 된다. 이 과정에서 해독이 불가능해지는 것이다.
Assumption
- All frames involved in a collision are lost
- The broadcast channel is wasted during the collision interval
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해서 multiple access protocol 이라는 protocol을 약속한다. 이를 통해 shared broadcast channel에 transmission을 하는 것을 규제하게 된다.
adapter 를 통해서 접근한다는 점을 주의해야 한다.Multiple access protocol
Multiple Access problem을 해결하기 위해서 여러 가지 접근방법이 있으나, 다음 3가지로만 구분하려고 한다.
- Channel partitioning protocols : TDM (2G), FDM (~1G), CDM (3G)
- Random access protocol : ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD
- Taking-turns protocols : Token Ring
이를 하나씩 살펴보기에 앞서, 다음과 같은 desirable characterisitc을 가진다고 가정한다. (단, broadcast channel의 bandwidth(data rate)은 R이다.)
- When only one node has data to send, that node has a throughput of R bps
- When M nodes have data to send, each of theses nodes has a throughput of R/M bps.💡항상 throughput이 R/M가 되는 것이 아니라 평균적인 throughput임에 주의하도록 하자.
- The protocol is decentralized; that is, there is
no master nodethat represents a single point of failure for the network→ 즉, 하나의 노드가 실패하더라도 전체 시스템에 치명적인 영향을 주지 않는다는 의미이다. 비트코인과 같은 암호화폐 네트워크에서 핵심적인 기능으로 사용된다.
- The protocol is simple, so that it is inexpensive to implement
추가적으로 여러가지 network 상황들이 존재한다. (예를들어 wired, wireless network). 따라서 하나의 솔루션이 아니라 각각의 네트워크 환경과 요구사항에 맞게 최적화된 솔루션들이 달라지게 된다는 점을 주의해야 한다.
그러면 하나씩 살펴보도록 하자.
Channel Partitioning
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)

예를 들어 해당 channel이 N개의 node를 지원하고, 해당 channel의 bandwidth가 R bps라고 가정하자.
이 방식의 경우에는 시간을 time frame 로 나누고 해당 time frame을 N개의 time slot으로 나눈다. 이렇게 나눈 time slot을 N개의 node들 중 하나에 분배한다. 그리고 각 노드들은 할당받은 time slot에 대응되는 시간에만 channel에 transmission할 수 있다.
Pros
- Perfectly fair
→ 각 node들은 frame 시간동안 R/N bps로 transmission할 수 있으므로
Cons
- 다른 node들이 channel에 transmission을 시키지 않아도 R/N bps로 bounded된다는 것
- 모든 node들이 자신에게 할당된 time slot을 기다려야 한다는 점
→ 극단적으로 해당 node만 transmission시키고 싶은 상황에서도 자신 차례까지 기다려야 한다.
Frequency-division Multiplexing (FDM)
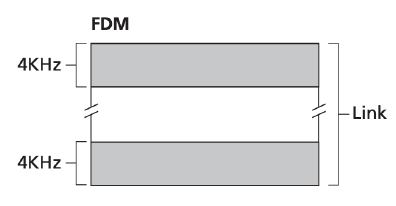
예를 들어 해당 channel이 N개의 node를 지원하고, 해당 channel의 bandwidth가 R bps라고 가정하자.
FDM의 경우 TDM와 달리 bandwidth인 R bps를 frequency 를 기준으로 노드의 수인 N으로 나눈다. (각각의 bandwidth는 R/N bps이다.) 이후, 각 frequency를 각 node에 할당한다.
Pros
- Perfectly fair
→ 각 node들은 frame 시간동안 R/N bps로 transmission할 수 있으므로
Cons
- 다른 node들이 channel에 transmission을 시키지 않아도 R/N bps로 bounded된다는 것
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)

각 node별로 서로 다른 code 를 할당한다. 이를 활용하여 transmit할 data bit를 encoding한다.
orthogonal codePros
- code를 잘 선택하면
동시에여러 노드들이 transmission 시켜도 상관없다.→ 서로 다른 코드 사이에서 발생하는 상호 간섭으로부터 원하는 신호만 추출해내려면 해당 신호의 코드만 알면 된다. 따라서 모든 사용자가 동시에 같은 주파수 대역을 공유해서 정보를 전달할 수 있다.
Random Access Protocols
In a random access protocol, a transmitting node always transmits at the full rate of the channel, namely, R bps.
When there is a collision, each node involved in the collision repeatedly retransmits its frame until its frame gets through without a collision
단, 만약 collision이 발생하면 바로 다시 보내는 것이 아니라 random delay 만큼을 기다린다. 이때 random delay는 노드마다 독립적으로 선택된다.
→ with random delay probability p
구체적으로 알아보기에 앞서 용어를 정리하도록 하자
Efficiency
Definition
Fraction of successful channel use
Example
- probability of one and only one node transmitting in a random access scheme
- the probability that a time slot is used in a TDM scheme
Slotted-ALOHA
진행하기에 앞서 몇 가지를 전제하도록 하겠다.
- All frames consist of
exactlyL bits
- Time is divided into slots of size L/R seconds (that is, a slot equals the time to transmit one frame)
- Nodes start to transmit frames only at the beginning of slots💡즉, slot이 시작할 때만 frame을 전송할 수 있다는 것이다. 이를 통해 collision을 최소화시킨다.
- The nodes are
synchronizedso that each node knows when the slots begin.
- If two or more frames collide in a slot, then all the nodes detect the collision event before the slot ends.
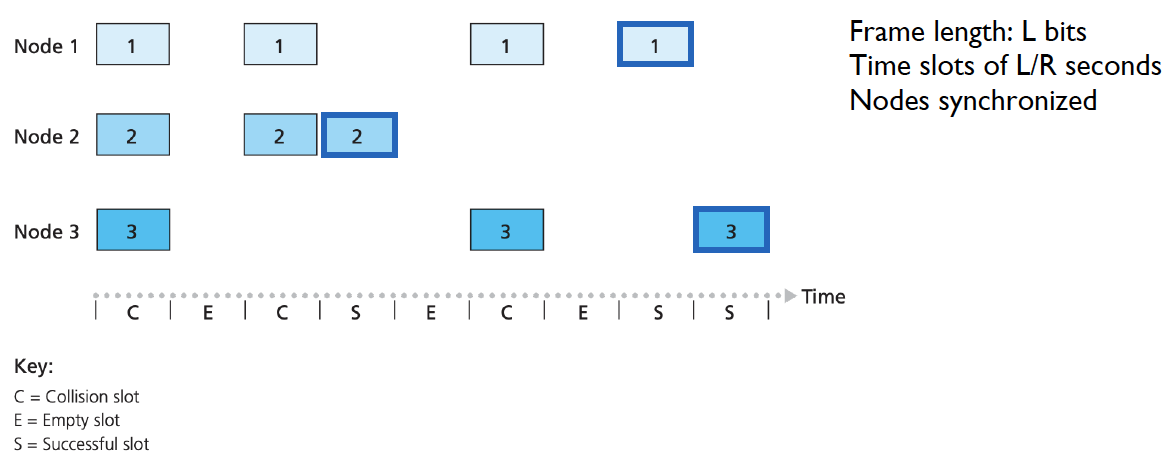
과정은 다음과 같다.
- When the node has a fresh frame to send, it waits until the beginning of the next slot and transmits the entire frame in the slot
- If there isn’t a collision, the node has successfully transmitted its frame and thus need not consider retransmitting the frame (The node can prepare a new frame for transmission, if it has one)
- If there is a collision, the node detects the collision before the end of the slot. The node retransmits its frame in each
subsequence slot with probabilitypuntil the frame is transmitted without a collision💡즉 앞서 언급한 것처럼 바로 보내는 것이 아니라 p의 확률로 이후 slot에 할당해서 transmission시키는 것이다. 만약 (1−p)가 걸린다면 skip the slot and toss the coin again in the next slot해주면 된다. (그림에서 확인할 수 있는 것처럼 해당 time slot을 건너뛰게 된다.)💡추가적으로 이러한 collision toss는 node별로independent하게 진행된다.
Pros
- Unlike channel partitioning, this allows a node to transmit continuously at the full rate, R, when the node is the only active node💡TDMA, FDMA의 경우에 비해서는 channel의 bandwidth를 전부 활용할 수 있다는 점에서는 장점이 있다.
- Highly decentralized, because each node detects collisions and independently decides when to retransmit
Cons
- Require the slots to be synchronized in the nodes
- Certain fraction of the slots will have collisions and will therefore be
wasted→ 위 그림에서 맨 처음 시간 상황을 참고해주면 된다.
- A certain fraction of the slots will be
emptybecause all active nodes refrain from transmitting as a result of the probabilistic transmission policy→ 위 그림에서 2번째 시간 상황을 참고해주면 된다.
이때 1개의 node만 transmit된 경우를 successful slot 이라고 한다.
Maximum efficiency
N : number of nodes
p : the probability of the transmission
We want to find p which maximizes
where N approaches infinity
where p∗ is a optimal probability
Therefore
ALOHA
Same principle as slotted ALOHA but not synchronized among the nodes

Maximum efficiency
N : number of nodes
p : the probability of the transmission
→ 추가적으로 1개의 frame을 보내는데 unit of time이 걸린다고 가정한다
We want to find p which maximizes
where N approaches infinity
절반밖에 안나온다는 점을 주의해야 한다. 이는 decentralized하게 되면서 지불하는 cost라고 이해해주면 된다.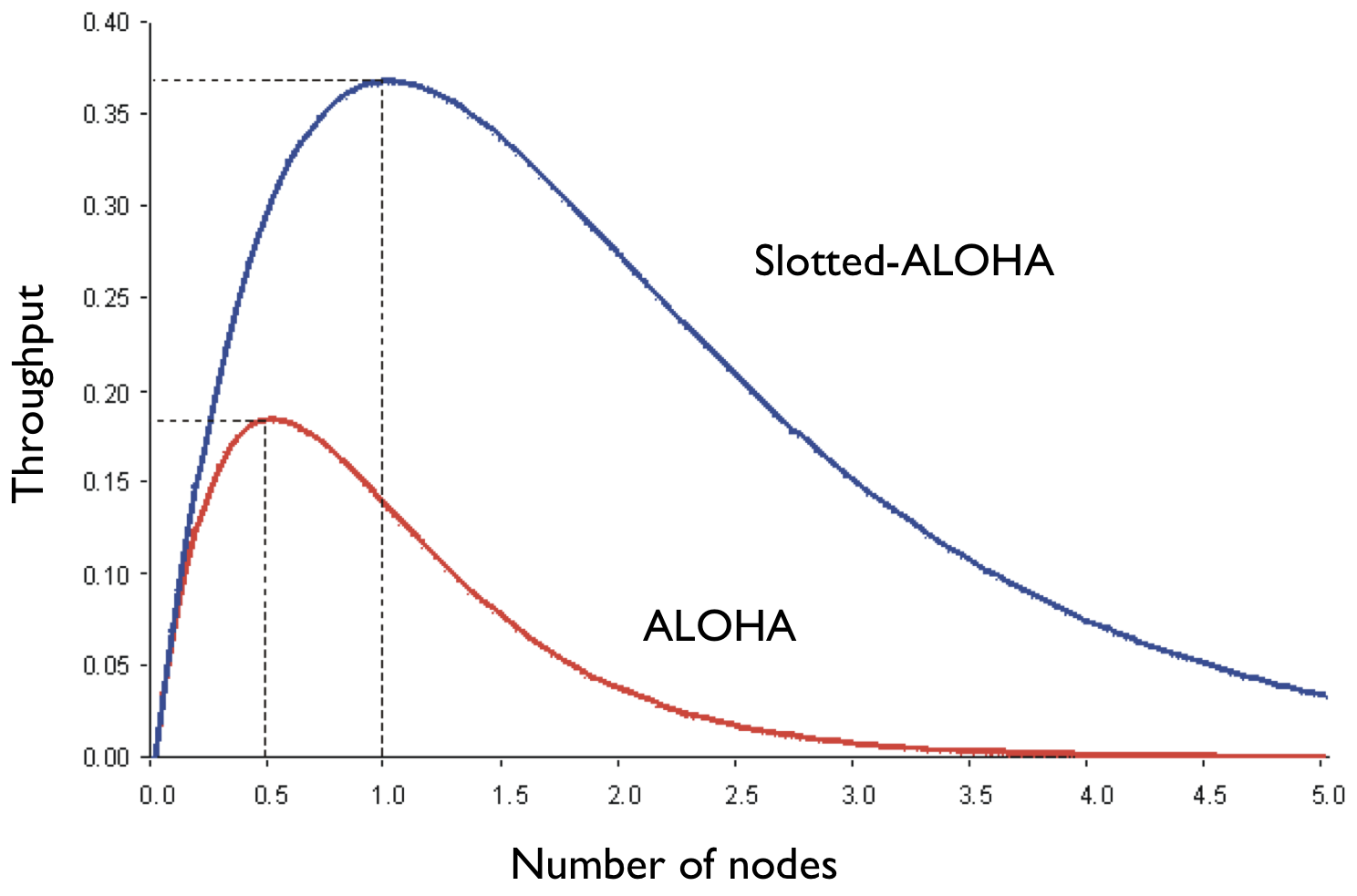
CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) / CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection)
앞서 살펴본 ALOHA와 Slotted ALOHA는 기본적으로 다른 노드들의 행동에 대해서 신경쓰지 않는다. 결과적으로 장점도 있기는 하지만, 이 때문에 collision이 근본적으로 발생하게 되고 이에 따라 retransmission을 진행해야한다.
잘 생각해보면 사람의 경우 이러한 상황에서 대처하는 2가지 방법이 있다.
- Listen before speaking
- If someone else begins talking at the same time, stop talking
즉, 말하기전에 먼저 듣고 누군가가 동시에 말하기 시작하면 그만 말하는 것이다.
wired Ethernet Protocol에서 쓰는 방식으로 WiFi Protocol에서는 CSMA/CA를 사용한다. 왜냐하면 무선환경에서는 Collision Detection하는 것이 어렵기 때문에 Collision Avoidance로 전략을 바꾼 것이다.이를 네트워크에 대응하면 다음과 같다
carrier sensing: sensing—a node listens to the channel before transmitting💡일정 시간동안 다른 node가 transmission하고 있지 않으면 transmission하는 방식이라고 이해하면 된다.💡하지만, 거의 동시에 transmission을 진행하면 carrier sensing만으로는 이를 해결할 수 없다. 이에 등장한 개념이 collision detection이다.
collision detection: a transmitting node listens to the channel while it is transmitting💡transmitting하고 있는 도중에 다른 node가 transmitting하고 있는 것을 감지하면 random time만큼을 기다린 후 sense와 transmit과정을 반복하게 된다. (random time을 기다리는 이후는 추가적인 collision 발생가능성을 낮추기 위함이다.)
이러한 특성때문에 pure ALOHA나 slotted ALOHA보다 더 효율적으로 처리를 진행하게 된다. 왜냐하면 위 방식은 충돌이 전체 프레임이 전송된 후에만 감지되기 때문이다.
이때, collision detection을 수행하면 CSMA/CD (Collision Sense Multiple Access with Collision)이고, 아니면 CSMA (Collision Sense Multiple Access)라고 불린다.
Example
- Horizontal axis : the position of the each node
- Vertical axis : time
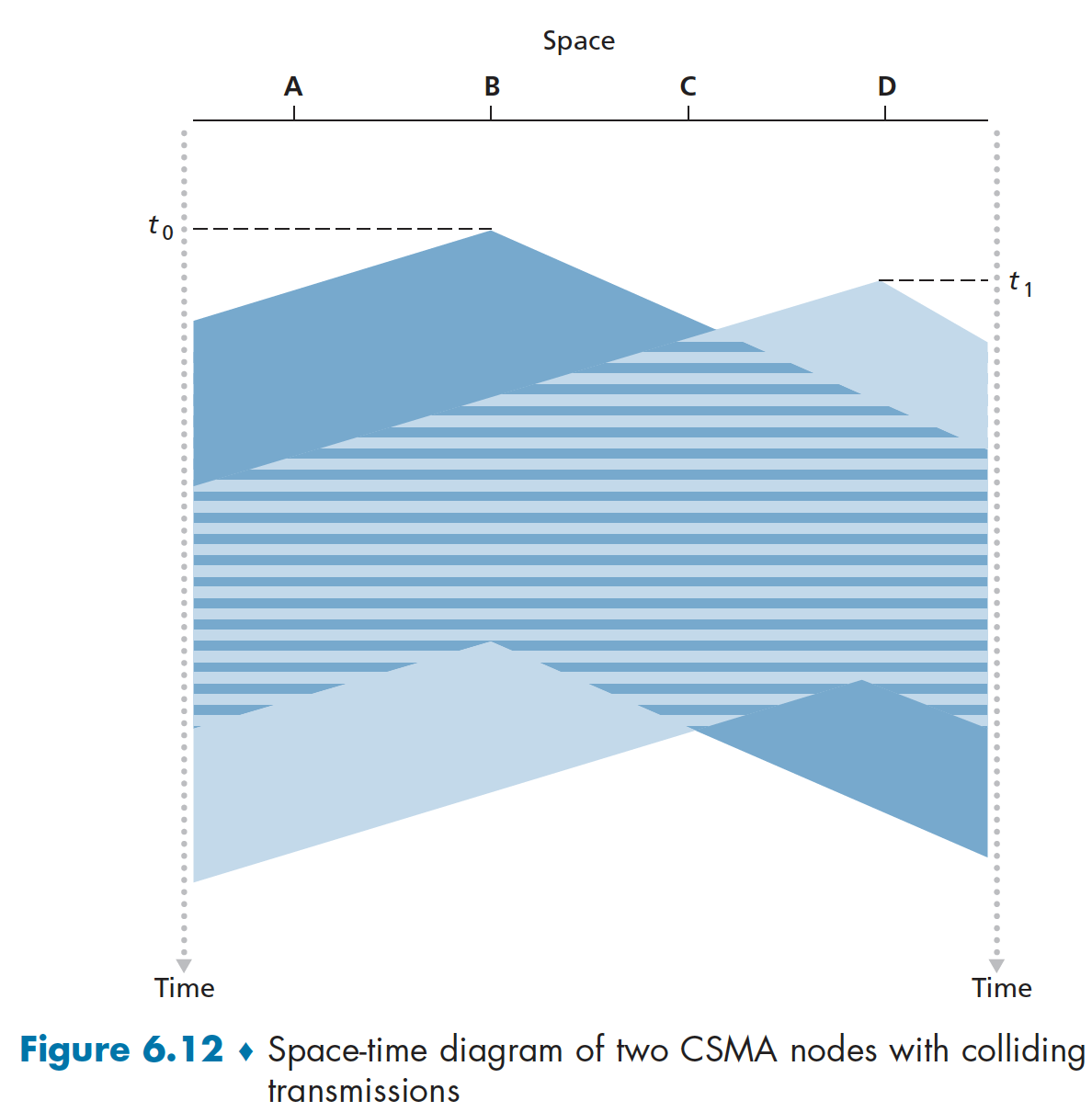
위 그림에서 t0에 B는 idle이기때문에 양방향으로 transmission시킨 상황이다. 이때, t1상황에서는 B가 frame을 transmission시켰음에도 불구하고 해당 정보가 D에 도달하지 않았기 때문에 D 또한 transmission을 시킨다. 이떄문에 collision이 발생한 상황이다.
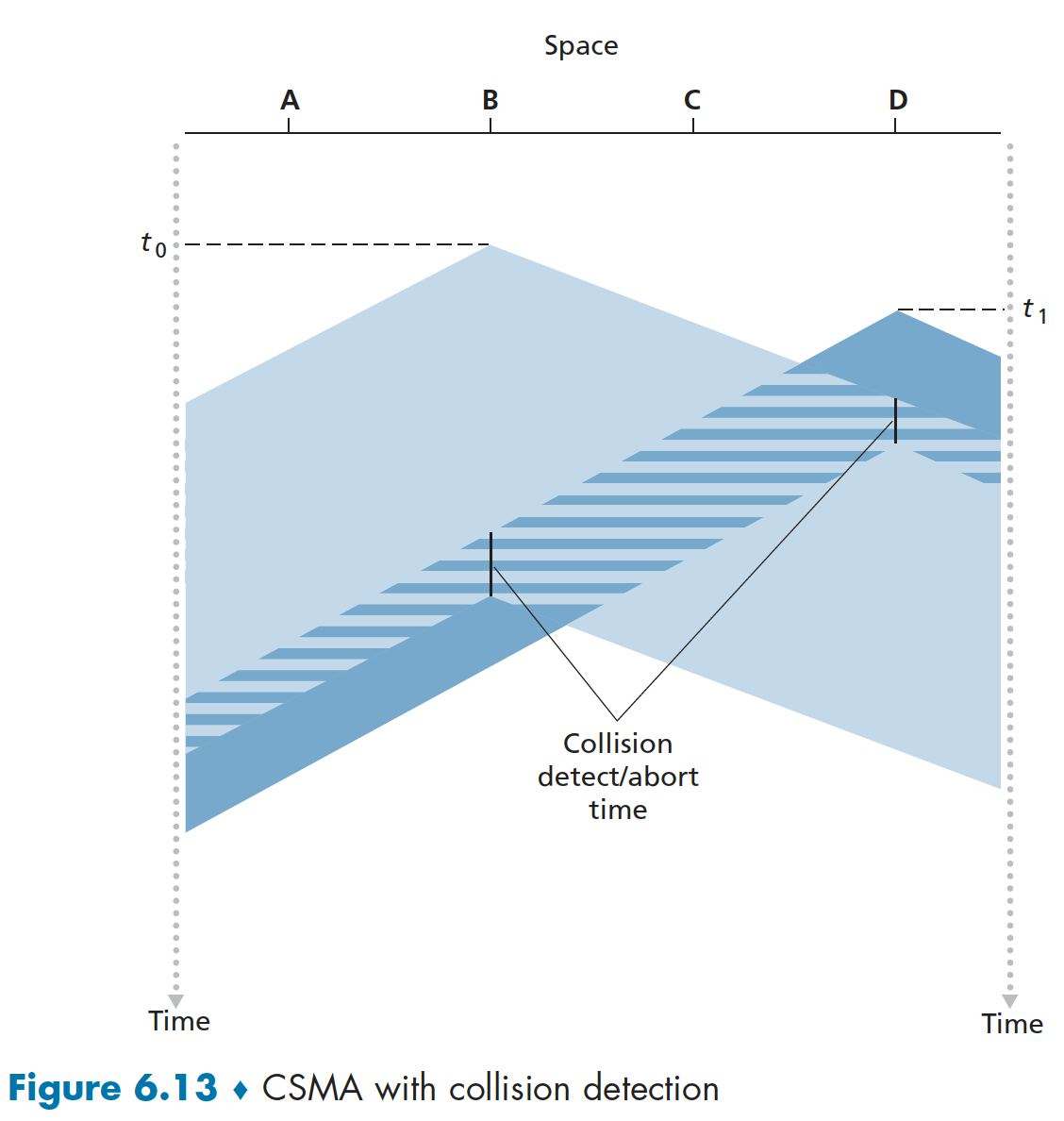
위 그림은 collision을 detect한 순간 transmission을 멈추는 것이다.
단, 멈추기까지 약간의 collision detection/abort time 이 요구된다. 해당 시간 이후에 바로 transmission을 멈추게 된다.
추가적으로 collision을 detect한 이후 네트워크상의 다른 모든 장치들에게 충돌이 발생했음을 알리기 위해 특별한 신호인 Jam signal를 전송한다. 이 신호를 받은 다른 장치들도 자신의 전송을 중단합니다.
noise. The device continues to transmit this noise onto the shared communication medium for a certain period of time.Because all devices on the network segment share the same communication medium, they can all hear this noise. When they detect this noise, they understand that there has been a collision on the network. (즉, packet 형태로 전송하는 것이 아니기 떄문에 MAC broadcast나 IP broadcast 방식이랑은 차이가 있다. 단지 noise를 보내고 이를 detect하는 것이다.)
만약 Collision이 발생했다면 얼마나 많은 시간을 기다리고 sense-and-transmit 과정을 진행해주어야 할까? 해당 시간이 너무 길면 비효율적이고, 너무 짧으면 collision이 날 확률이 증가하기 때문이다.
→ binary exponential backoff 를 사용하면 이를 쉽게 해결할 수 있다.
Binary exponential Backoff
n : 이전까지 발생한 collision의 횟수
각 node들은 {0,1,…,2n−1} 중에 1개를 선택한다. (고른 값을 K라고 하겠다.)
왜 이름이 Binary exponential Backoff일까? 왜냐하면 충돌이 계속 발생할 경우 binary exponential하게 증가하기 때문이다. 즉, 대기 시간의 최댓값이 2배만큼 계속 커지기 때문에 binary exponential이고, backoff는 대기한다는 측면에서 유래하였다.
Ethernet의 경우에는 기다리는 시간을 K⋅512 (bit time)으로 설정하게 된다.
추가적으로 CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) 방식에서는 각 노드가 새로운 프레임을 전송할 준비를 할 때마다 CSMA/CD 알고리즘이 실행되며, 이때 최근에 발생했던 어떠한 충돌도 고려하지 않는다. 따라서 새로운 프레임을 가진 노드는 다른 노드들이 충돌 후 지수 백오프 상태(exponential backoff state)에 있어도 즉시 성공적인 전송을 시도할 수 있습니다. 이런 방식은 네트워크의 전체적인 효율성을 향상시키는데 기여한다.
Efficiency
해당 efficiency 공식은 꽤나 직관적이다.
- 앞서 언급한 것처럼 propagation delay가 0으로 간다면 efficiency는 1로 수렴한다. 왜나하면, collision을 바로 인식해서 transmission을 즉시 중단할 수 있기 때문이다.💡앞의 예시를 참고하도록 하자. 결과적으로 t1 시점에서 collision을 인식하지 못한 근본적인 이유가 propagation을 하는 과정에서 시간이 걸리기 때문이었다.
- 추가적으로 transmission delay가 매우 커진다면 efficiency는 1로 수렴한다.💡대부분의 시간 동안 채널은 데이터를 전송하는 데 사용되고 있으므로 낭비되는 시간(즉, 아무런 데이터도 전송되지 않는 시간)이 줄어들기 때문에 efficiency가 1로 수렴한다고 이해하면 된다.

Taking-Turns Protocols
앞서 언급한 multiple access의 이상적인 조건을 다시 알아보도록 하자
- when only one node is active, the active node has a throughput of R bps💡즉, 혼자 이용하고 있을 때는 모든 bandwidth를 다 쓸 수 있어야 한다는 것이다.
- when M nodes are active, then each active node has a throughput of nearly R/M bps💡즉 M개의 node와 공유하고 있는 경우 평균적으로 throughput을 R/M만큼 보장해주어야 한다는 의미이다.
하지만, ALOHA와 CSAM의 경우에는 1번째 조건은 만족하지만, 2번째 조건을 만족하지 못한다.
→ 이러한 문제점을 해결하고자 등장한 protocol이 taking-turns protocols 이다.
기본적으로 여러가지 variation이 존재하지만 2가지만 살펴보도록 하겠다.
Polling protocol
- 속한 노드들 중 하나를
master node로 지정한다.→ master node는
round-robin형태로 돌아가면서 지정한다.
- master node가 순서대로 노드들을 할당한다.
→ 단, master node에 문제가 생기는 경우에는 문제가 발생할 수 있고 polling delay가 발생할 수 있다는 점은 단점이다.
→ 반면 collision과 empty slot을 막을 수 있다는 점에서는 효율적이다.
Token passing protocol
이 방식은 polling protocol와 달리 master node가 존재하지 않는다. 대신 token 이라는 것이 존재해서, 이것들을 node들끼리 정해진 순서대로 교환한다.
이때, transmit할 frame이 존재하는 경우에만 해당 token을 가지고 있고 그렇지 않은 경우에는 다음 node에게 해당 token을 넘긴다.
→ 단, 1개의 node가 고장나거나 token을 받았음에도 불구하고 release를 하지 않는다면 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
→ 반면, decentralized하고 굉장히 효율적이라는 장점이 존재한다.
Note
The term 공유기 in the consumer market often refers to a device with Wi-Fi capabilities. Such routers typically perform three main roles:
- Switching Function: They provide multiple Ethernet ports to enable direct communication between multiple devices on a LAN (Local Area Network).
- Routing Function: They are responsible for the connection to the ISP (Internet Service Provider) and forwarding packets to external networks.Wi-Fi
- Access Point Function: They allow wireless devices to connect to the LAN.
So, in this sense, you can consider a 공유기 as a type of router. However, in strict networking terminology, "router" and "switch (or network switch)" refer to devices that perform different roles.
A router forwards traffic between networks. A switch (or network switch) transfers data between devices within one Local Area Network (LAN).
소중한 공감 감사합니다
